Name: ……………………. Age: …. Sex: Female
Education: Elementary school Handedness: Right DOB: …..
Informants:
Referred by: ………..
Reason for Referral: For the assessment of current level of pathology
Chief Complaints:
• Poor
• Difficulty in recalling answers during exams
• Difficulty in reading and writing
History of Present Illness:
Family history
The client lives in a joint family with her grandmother, grandfather, parents, younger sister (5th standard), her father’s elder and younger brother and their family’s respectively. Her father has well-functioning business. Since past few months various family issues have cropped up due to this. The sisters-in-law often get into quarrels which sometimes directly affects the client and sometimes indirectly in ways her mother interacts with her because of that. She feels less loved and neglected at times.
Family genogram
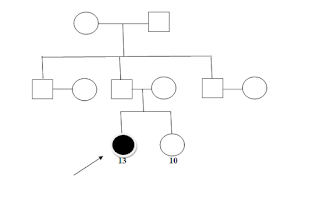 |
Personal history
Birth and Early Development
Childhood history
The client has always been very social and friendly and faced no trouble in making friends. She has always been very helpful and never got into trouble for her behavior. She can be
Scholastic History
The client started formal schooling at the age of 2.5years in .,….. She studied in …… till 1st standard and then joined her current school.Her parents thought she would get better personal attention there, but her grades have remained constant between ‘C’ to ‘D’ across both the schools. She has reported to have high exam anxiety, which further worsens her performance during exams.
Mental Status Examination
The client was well
Tests administered:
•
• NIMHANS Battery for Learning Disability
Test Findings:
Malin’s
On MISIC, the Full Scale I.Q was found to be 98 which indicate an average level of intellectual functioning.
The verbal scales reflect the child’s ability to work with abstract symbols, the amount and degree of benefit she has received from her educational background, verbal memory abilities and verbal fluency.
The verbal I.Q was found to be 97 indicating an average level of verbal intelligence. On the verbal subtests, the raw scores and the corresponding IQ were as follows:
Information: (17, 93) which indicates an average level of performance in verbal ability, intellectual curiosity and long-term memory.
Comprehension: (21, 116) indicating a bright normal level of performance in social judgment, reality awareness and understanding. He can grasp the social rules and regulations very well and has knowledge about moral codes.
Arithmetic: (7, 73) indicating a borderline level of performance in numerical reasoning and speed of numerical manipulation.
Similarities and Analogies: (11, 91) indicating an average level of performance in abstract intelligence and verbal reasoning and in categorizing meaningful relationships.
Vocabulary: (17, 105) indicating an average level of performance in language usage, word knowledge and verbal fluency.
The performance scales reflect the child’s degree and quality of nonverbal contact with the environment, the ability to integrate perceptual stimuli with relevant motor responses, the ability to work quickly and the capacity to work in concrete situations.
The performance I.Q was found to be 99, which indicates an average level of functioning
Picture completion: (10, 90) which indicates an average level of performance in the area of reasoning, attention to visual acuity (awareness about environmental details), visual discrimination and organization and long term visual memory.
Block design: (26, 99) indicating a normal level of performance in nonverbal concept formation, capacity for sustained effort, visual-motor- spatial coordination and manipulative and perceptual speed and abstract visual problem solving.
Object assembly: (19, 89) indicating a dull normal level of performance in her visual organizational ability, visual motor coordination with motor activity guided by visual perception and sensory motor feedback.
Coding: (71, 140) indicates a very superior level of performance in visuo-motor coordination, attention, short term memory, visual scanning and tracking.
Mazes: (11, 75) indicating a dull normal level of performance in visuo-motor planning, attention, concentration and vigilance and problem solving skills.
NIMHANS assessment battery for Specific Learning Disability
On NIMHANS Assessment Battery for Specific Learning Disability, she had been tested
Assessment of reading ability was done by asking the child to read out a given passage. There were substitutions for e.g. ‘
Skills for comprehension were assessed by asking questions about the read passage. Her reading comprehension was not grade appropriate and she could answer IV grade questions adequately. She gave inadequate answers to the questions at standard V, VI and VII. She could not answer
Her spelling ability was found to be at
In
In Arithmetic, her level of performance was
Summary of Findings:
The subject’s IQ on Malin’s Intelligence Scale for Indian Children was found out to be 98 which
In NIMHANS Index for Specific Learning Disability, the client was found to have disability in the areas of Reading, Spelling, Writing and Mathematics.
Impression:
Mixed learning disorder (Reading, Spelling, Writing and Mathematics)
Suggestions:
• Parental counseling
• Assisted learning with the help of teachers/parents
• Exercises that increase phonological awareness, to help her to learn and understand sound patterns associated with words
• Using
• Using cued-spelling techniques
• Use of mnemonics to memorize spellings
• Remedial teachings in comprehension
• Pre-teaching vocabulary using analogies
• Create own sentences and then look up the key words in the dictionary to confirm they have used correctly
• Helping her to relate to the passage to an experience, another book, or other fact, helping to make connections to personal experience, knowledge and previous reading.
• Remedial teaching in Mathematics.
• Acquiring competency and confidence in number concepts
• Understanding number system
• Recalling basic facts and formulae
•
•